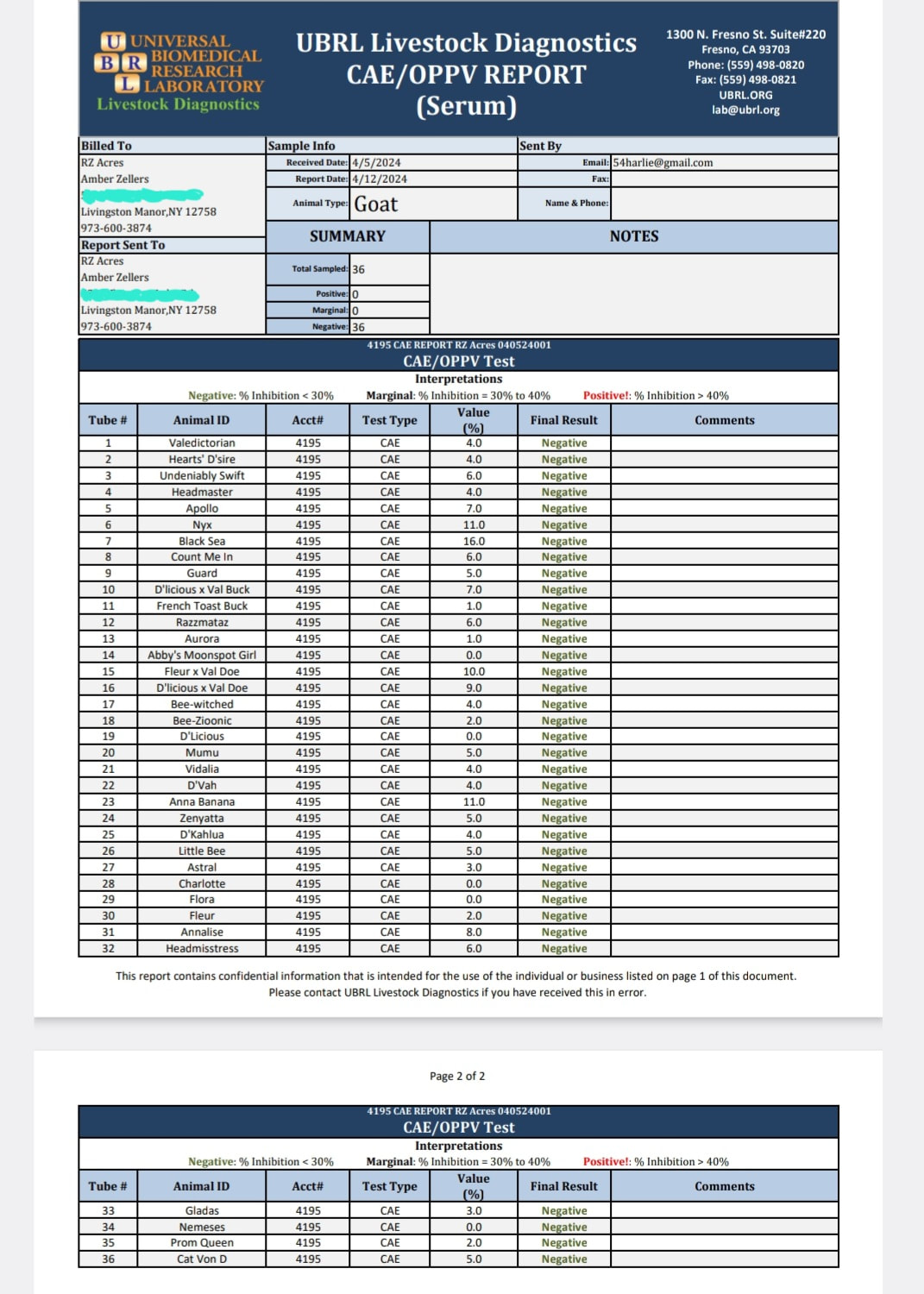
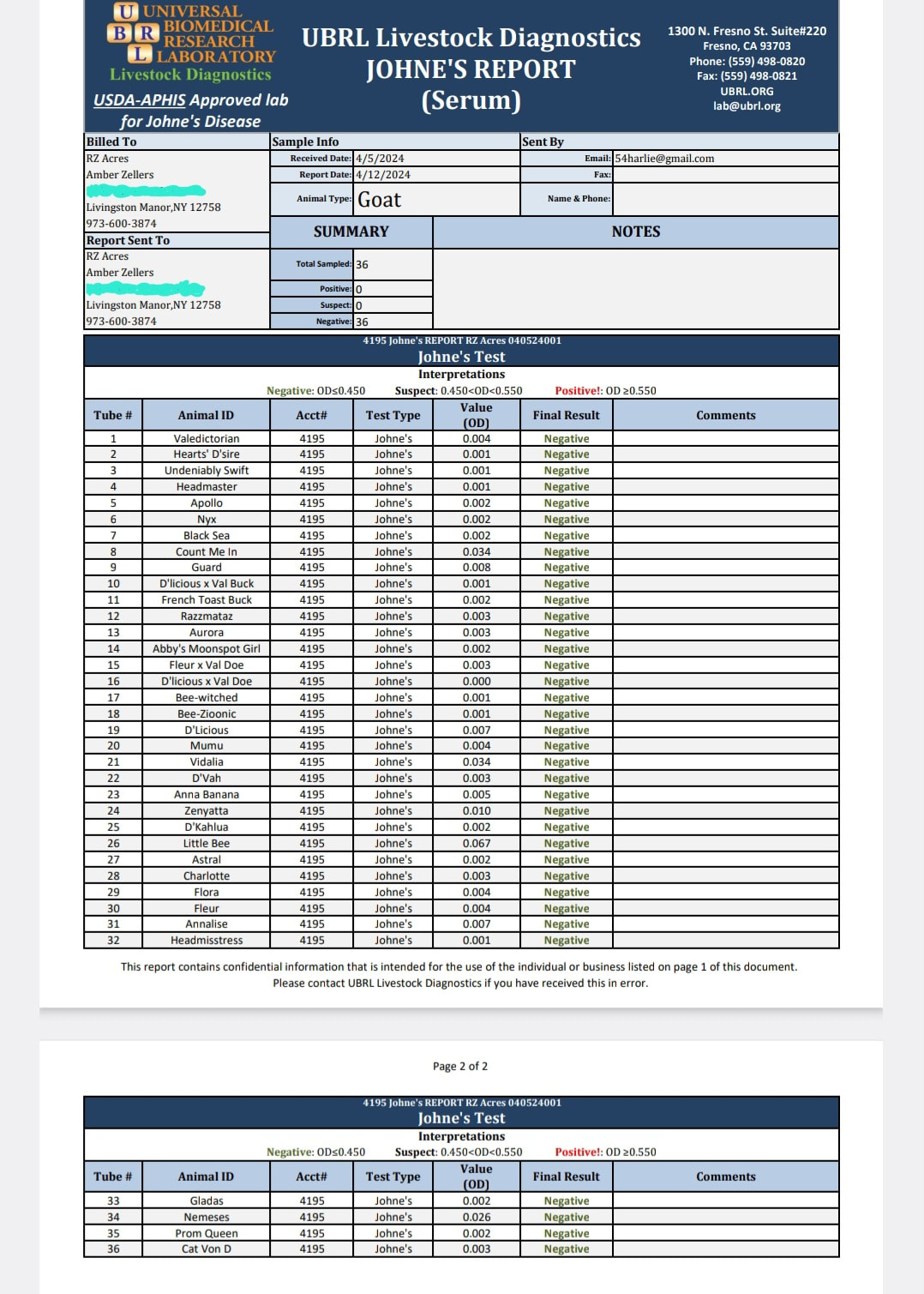
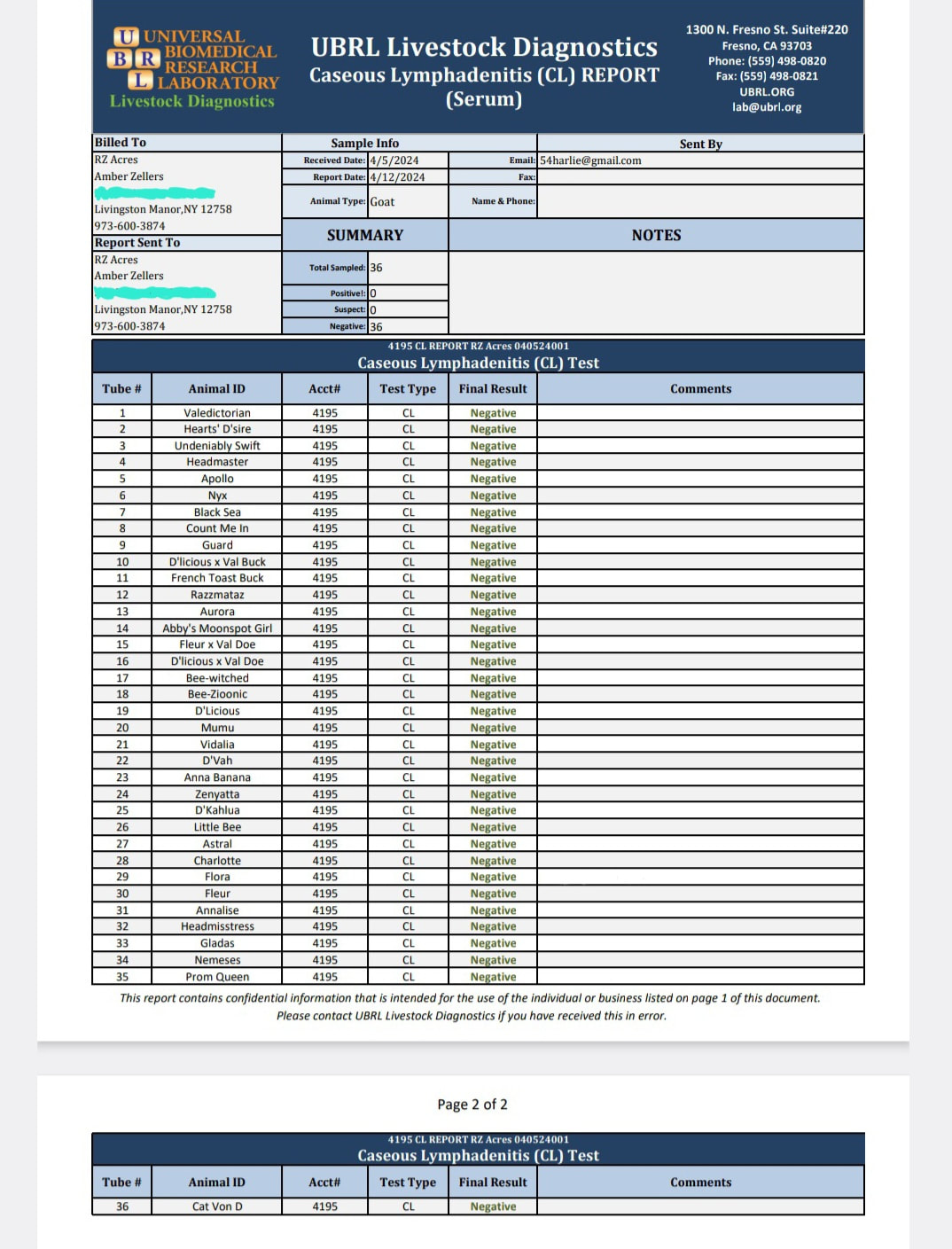
2024 test CAE, CL, & JOHNES-All negative
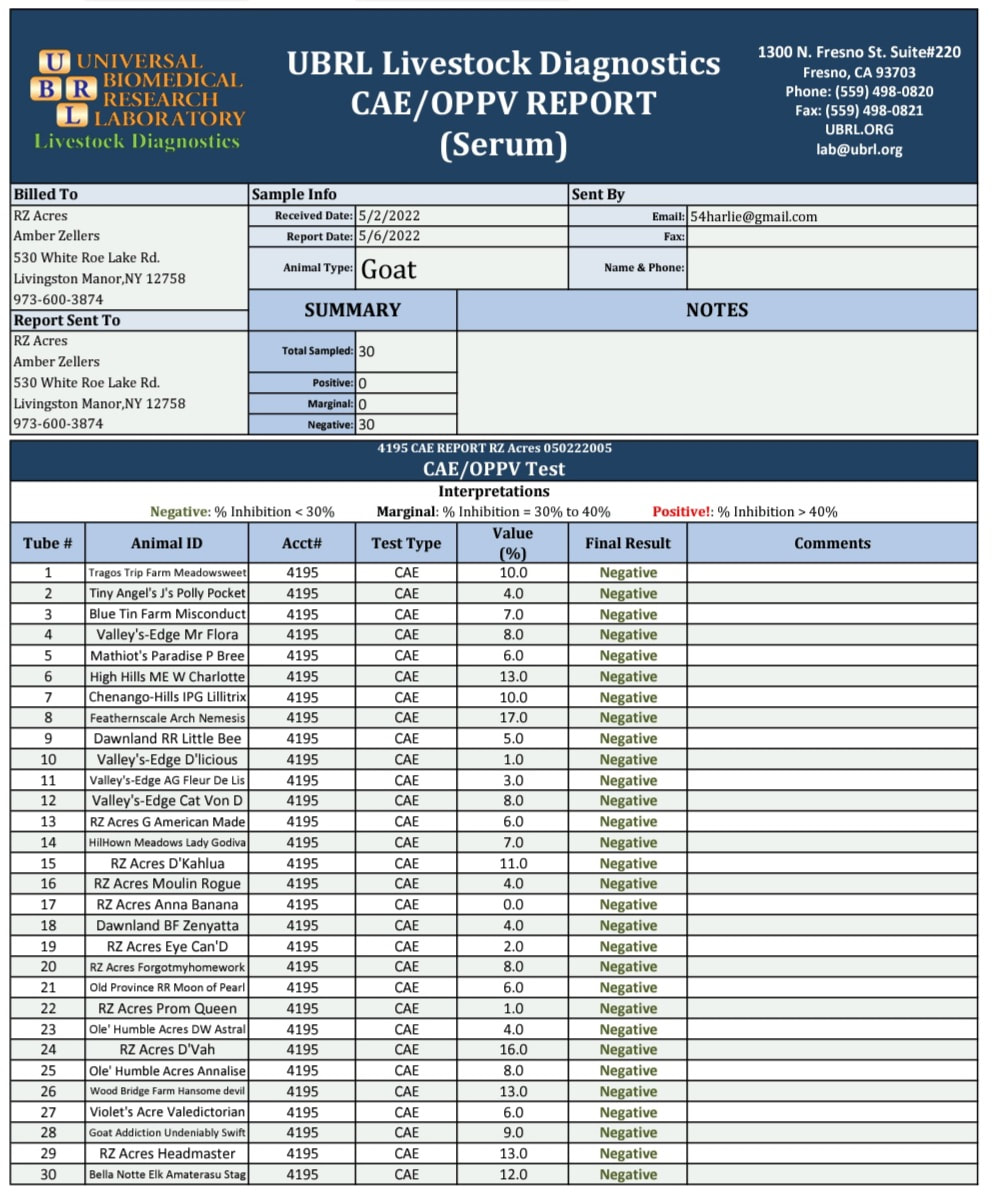
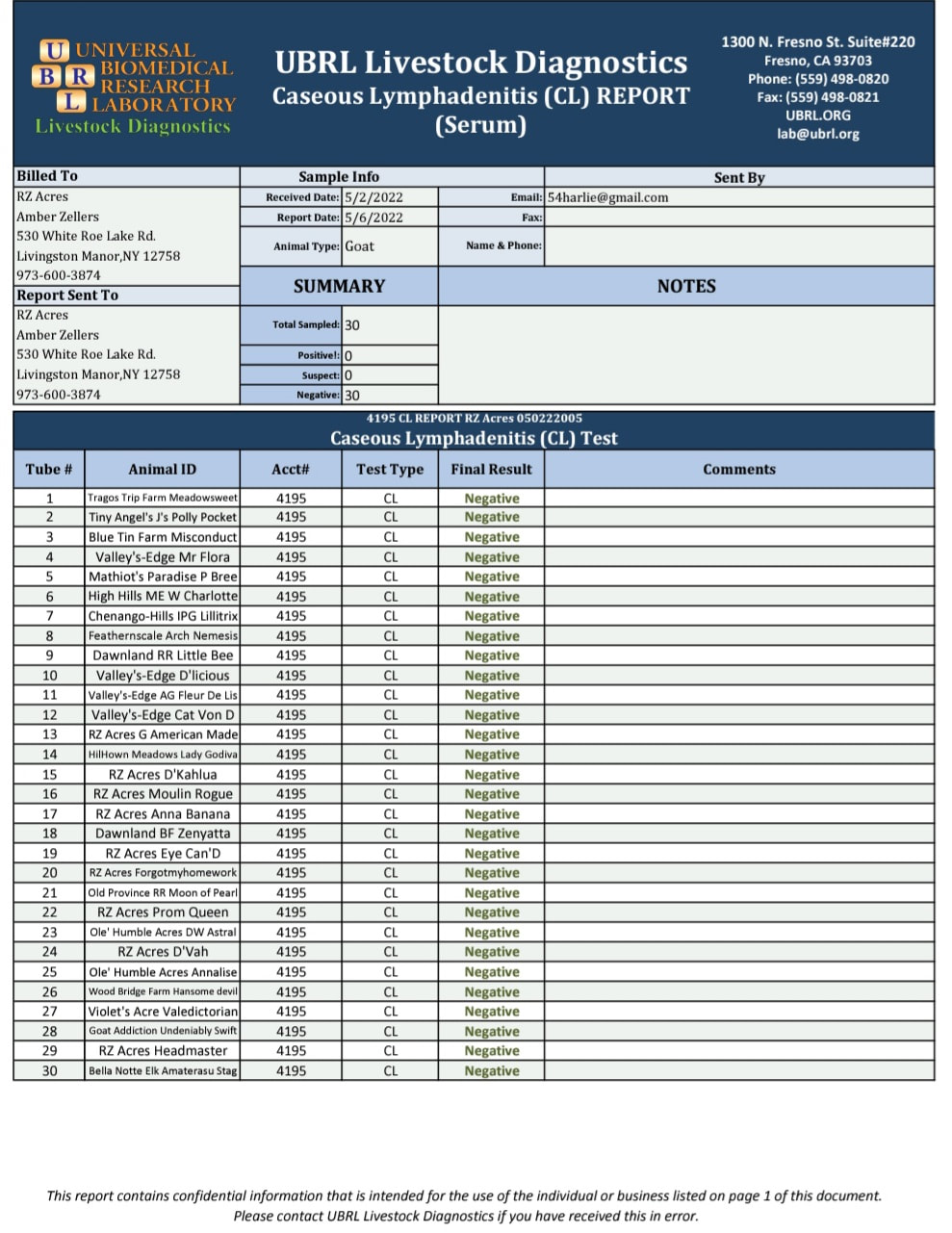
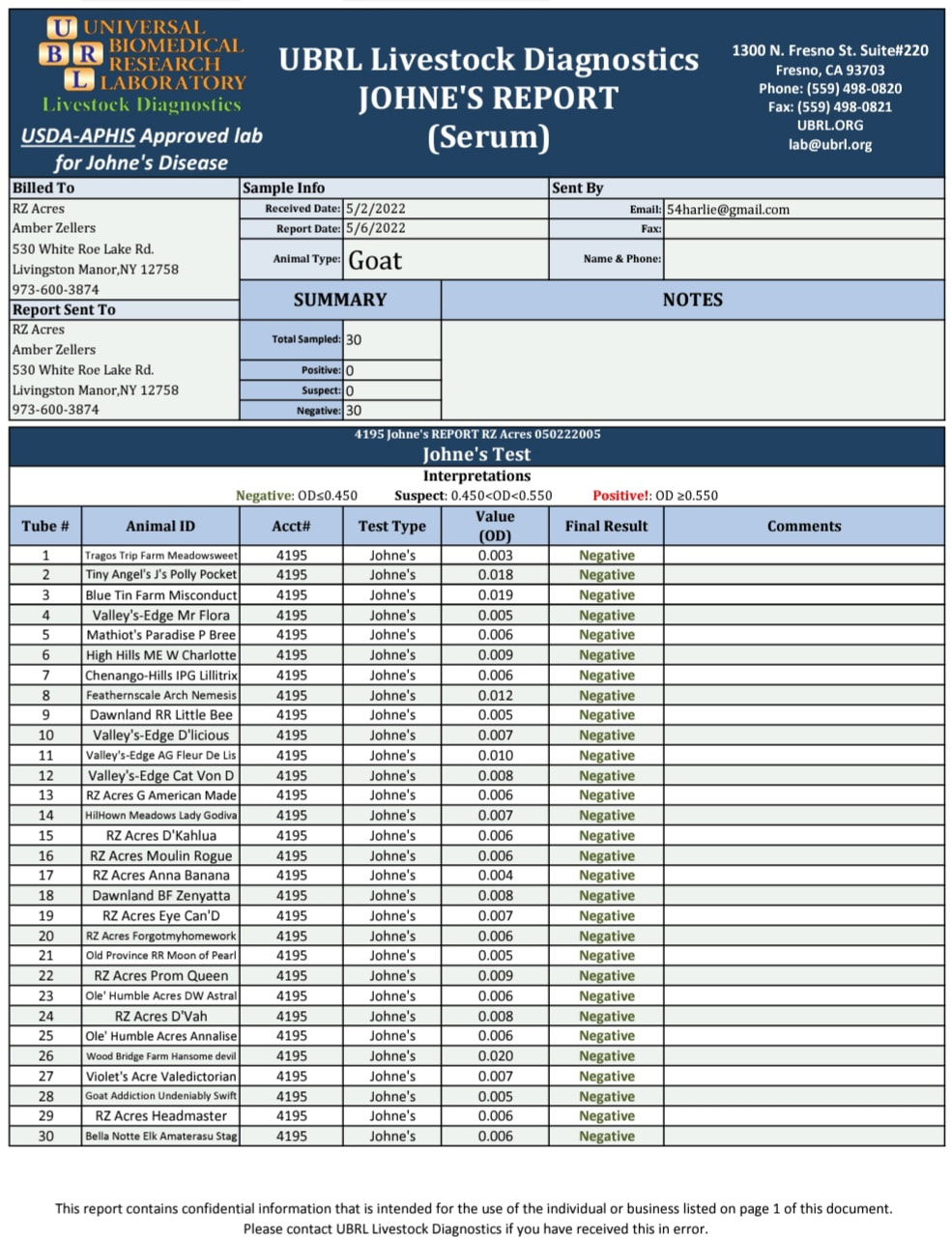
2022 tEST CAE, CL, & JOHNES
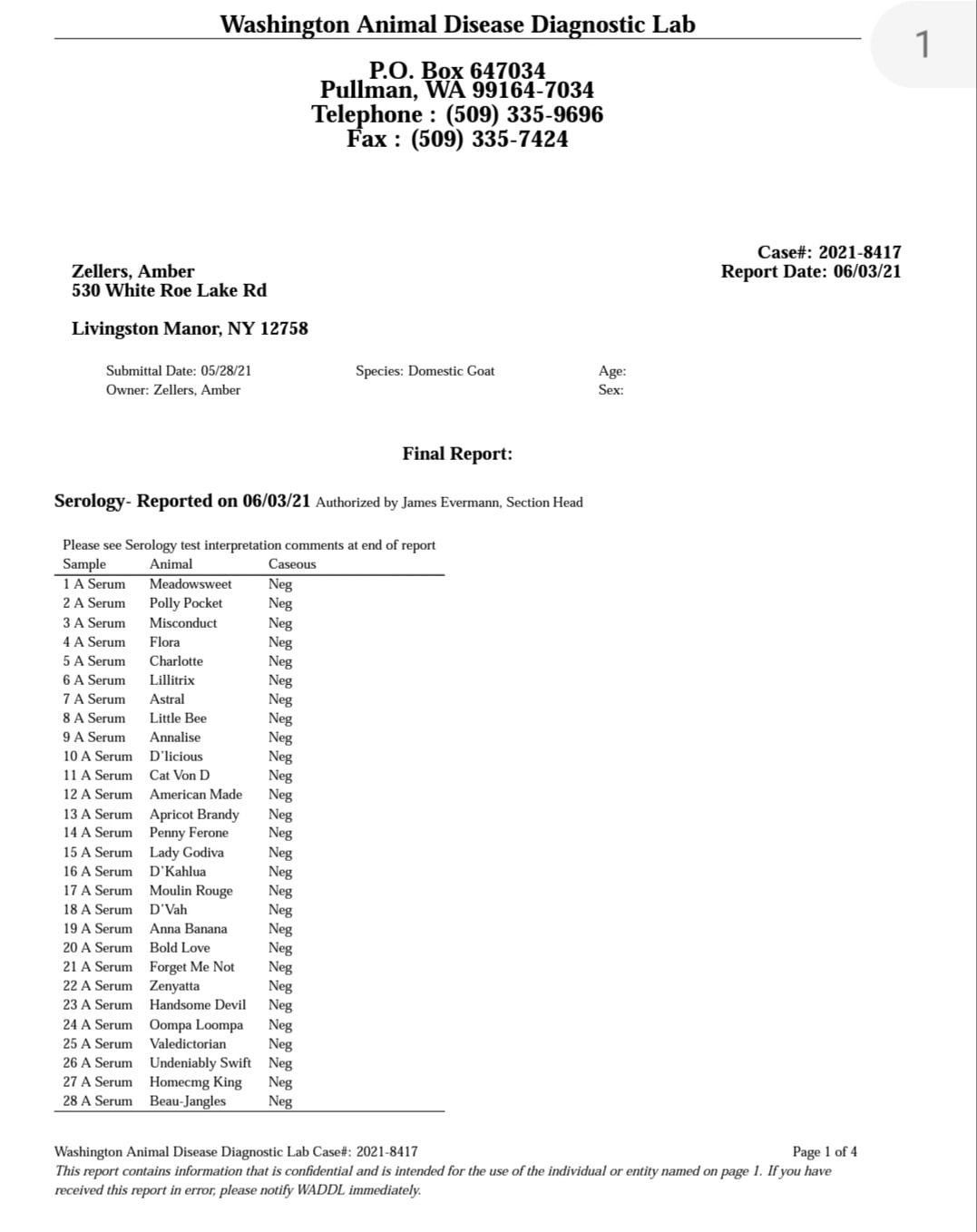
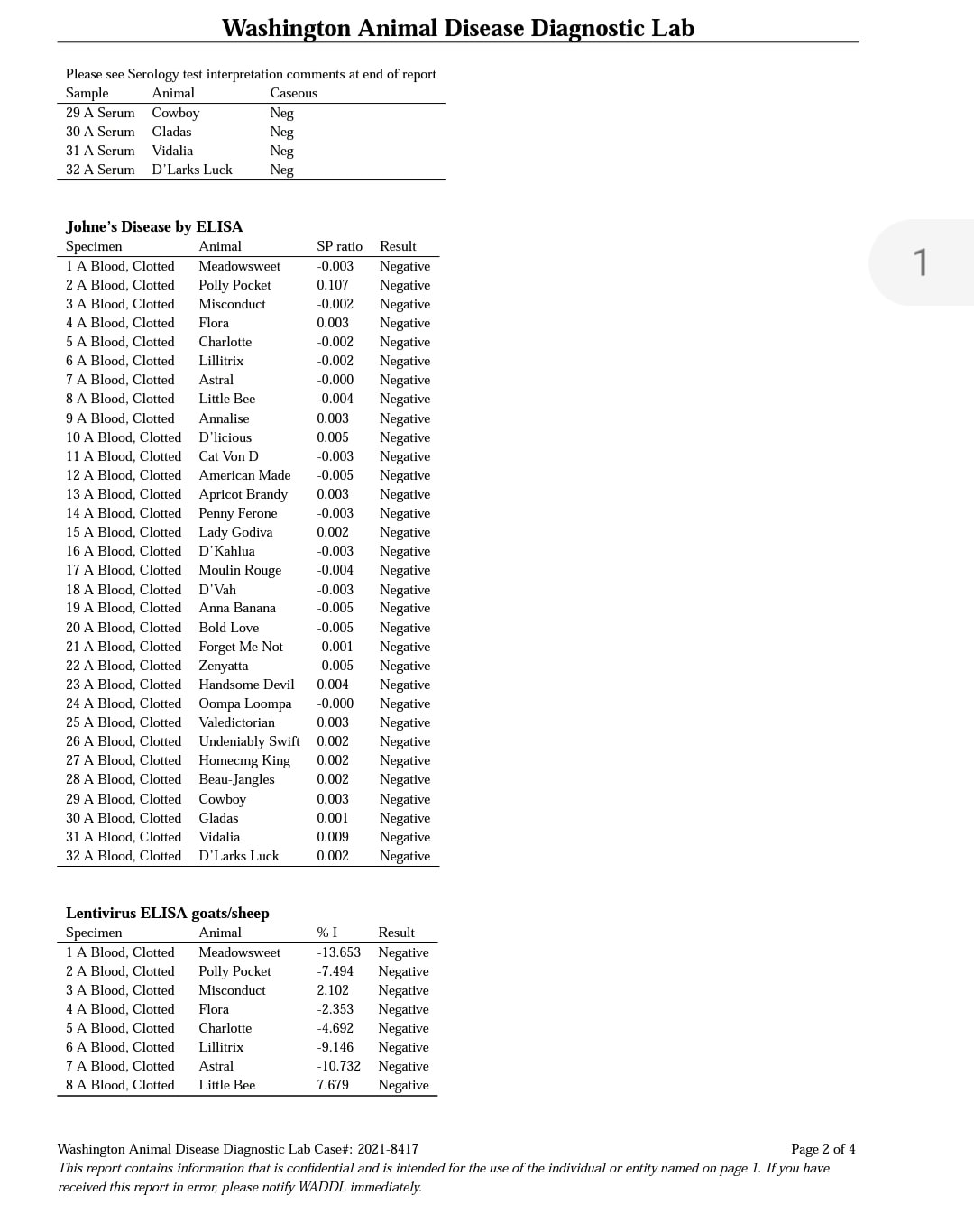
2021 test Cae,cl, & johnes
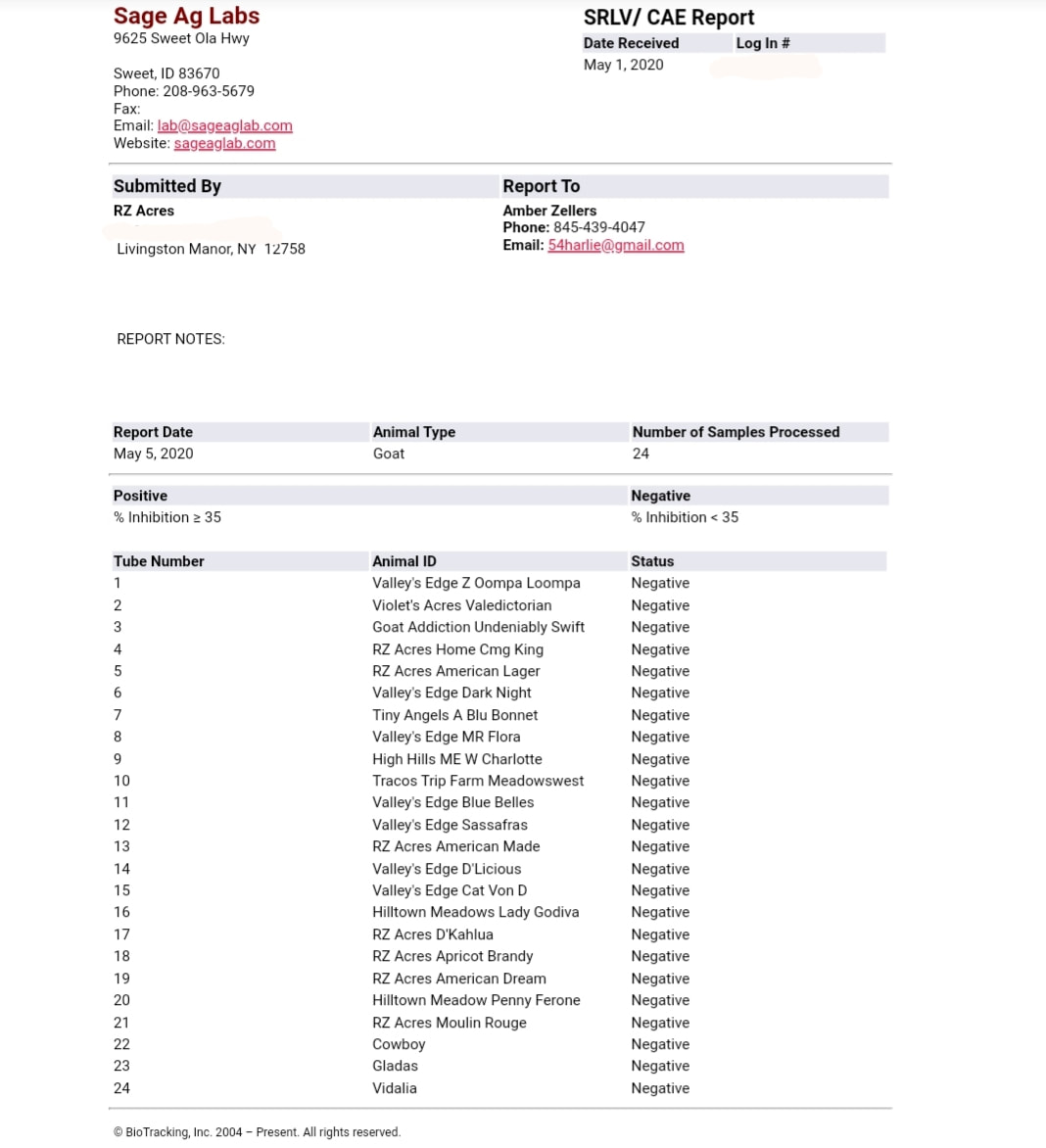
2020 CAE TEST- all negative
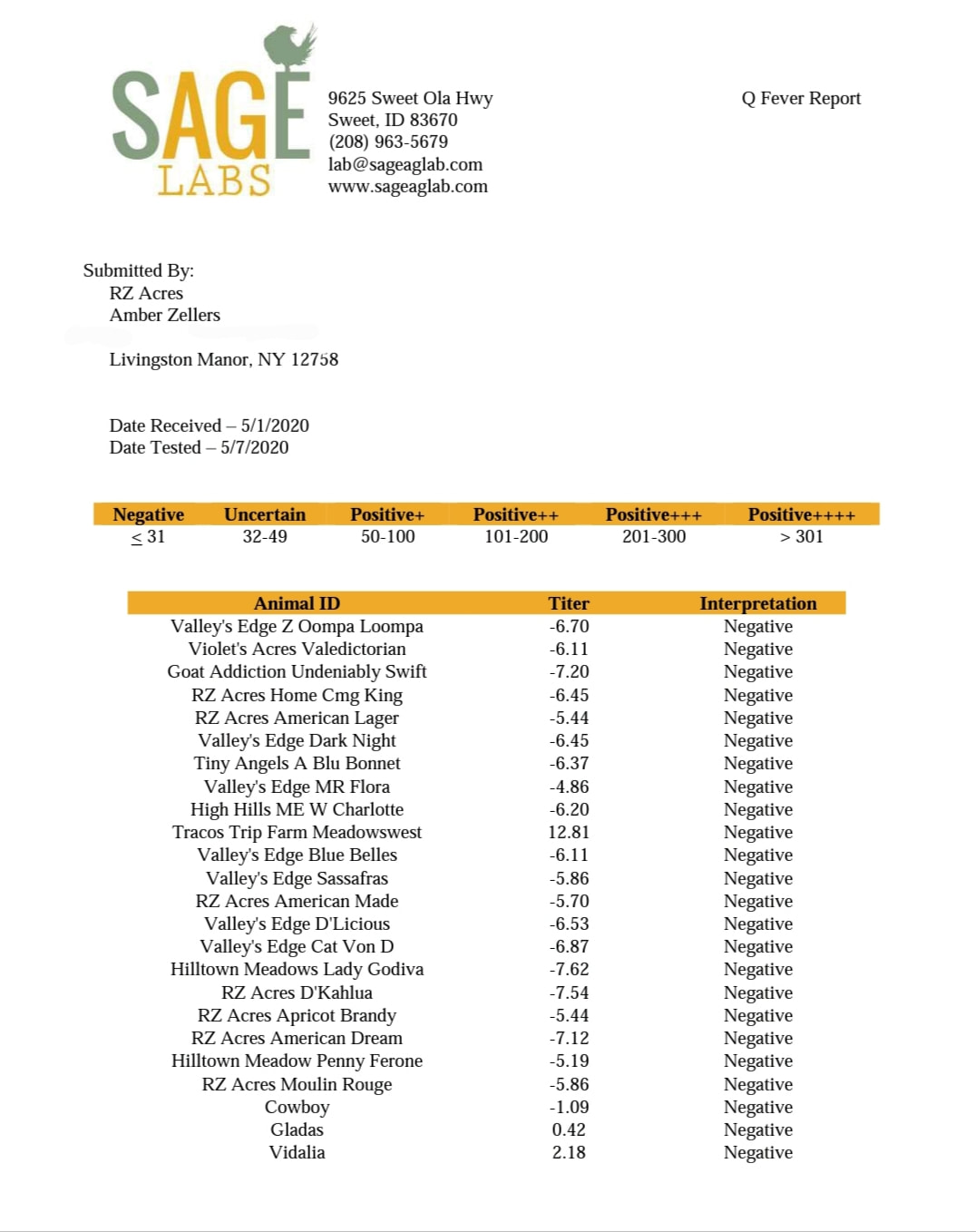
2020 Q Fever Test- all negative
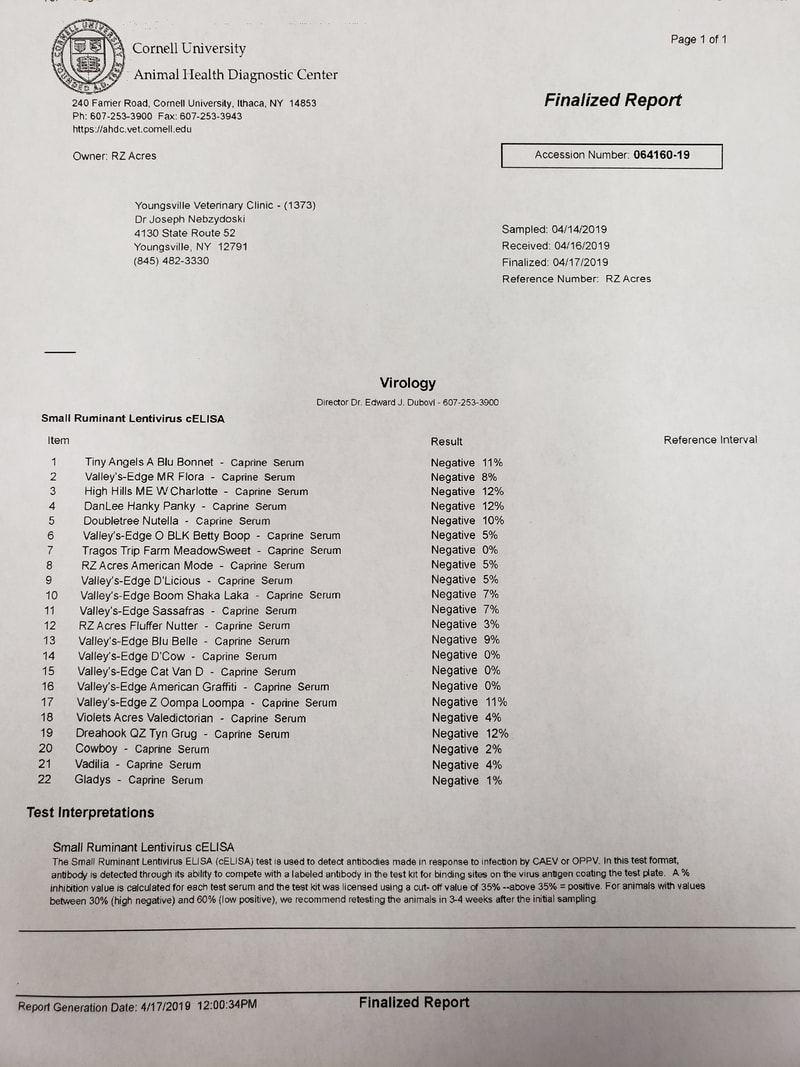
2019 Cae test results-all negative
Biosecurity practices we follow
What is CAE?
CAE (caprine arthritis encephalitis) is a viral disease caused by the lentivirus. It is closely related to ovine (sheep) lentivirus and cross species transmission can occur, especially through infected milk. CAE manifests in one of five different forms -- as arthritis, encephalitis, pneumonia, mastitis, or chronic wasting. The arthritis form is most often seen in adults, encephalitis in kids, and chronic wasting can appear solo or concurrently with any one of the other types. Transmission typically takes place when kids drink the milk from an infected dam, however adults can spread it to each another through bodily secretions including blood, feces, and saliva. Many cases are subclinical and due to the long incubation period of the virus it can take a couple years for a goat to become symptomatic. More info on CAE here and here.
What is Johne's?
Johne's (pronounced "yo-knees") is a gastrointestinal disease that occurs in ruminants, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). This bacteria lives in the small intestine of infected goats and is shed through the feces. Healthy goats become infected when they ingest the bacteria from contaminated pastures, hay feeders, water buckets, and/or teats. Like CAE, the incubation period for Johne's is also typically a few years. As the infection worsens, the lining of the small intestine becomes thick and loses its ability to absorb nutrients. Even though the goat continues to eat and have a good appetite they cannot maintain condition, becoming more and more emaciated until they die of starvation. More info on Johne's here and here.
What else can you test for?
Caseous lymphadenitis (CL)
Tuberculosis (TB)
Brucellosis
Q Fever
How to get your goats tested
Testing requires getting blood samples from your goats and submitting those samples to a lab. It's best to work with your veterinarian when possible.
- All of our goats are tested annually for CAE, CL, and Johne's at minimum.
- We do not offer buck services to the public.. besides the risk of your goat getting sick there are some unpleasant zoonotic diseases, such as chlamydia and sore mouth, that you could get as well!
- We only purchase from herds that practice good biosecurity as well. All new animals are quarantined and disease tested (if old enough) before joining the herd.
What is CAE?
CAE (caprine arthritis encephalitis) is a viral disease caused by the lentivirus. It is closely related to ovine (sheep) lentivirus and cross species transmission can occur, especially through infected milk. CAE manifests in one of five different forms -- as arthritis, encephalitis, pneumonia, mastitis, or chronic wasting. The arthritis form is most often seen in adults, encephalitis in kids, and chronic wasting can appear solo or concurrently with any one of the other types. Transmission typically takes place when kids drink the milk from an infected dam, however adults can spread it to each another through bodily secretions including blood, feces, and saliva. Many cases are subclinical and due to the long incubation period of the virus it can take a couple years for a goat to become symptomatic. More info on CAE here and here.
What is Johne's?
Johne's (pronounced "yo-knees") is a gastrointestinal disease that occurs in ruminants, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). This bacteria lives in the small intestine of infected goats and is shed through the feces. Healthy goats become infected when they ingest the bacteria from contaminated pastures, hay feeders, water buckets, and/or teats. Like CAE, the incubation period for Johne's is also typically a few years. As the infection worsens, the lining of the small intestine becomes thick and loses its ability to absorb nutrients. Even though the goat continues to eat and have a good appetite they cannot maintain condition, becoming more and more emaciated until they die of starvation. More info on Johne's here and here.
What else can you test for?
Caseous lymphadenitis (CL)
- Caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
- Effects lymph nodes and internal organs
- Causes abscesses
- Transmitted via ruptured abscesses or respiratory secretions (internal CL)
- Zoonotic (humans can contract CL from goats)
- Blood test for CL not very definitive on individual basis. Best practice to have culture done of pus if find abscess and to quarantine goat while wait for results.
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Caused by Mycobacterium bovis or M. tuberculosis
- Effects lungs, sometimes other organs
- Causes lesions
- Transmitted through raw milk, respiratory droplets, blood
- Zoonotic, effects all species of vertebrates
- Check TB infection status of your state and any states you purchase animals from.
- Testing recommended if you will be drinking milk raw. Must be done by veterinarian.
Brucellosis
- Brucella melitensis bacteria most common species in goats
- Causes late term abortions primarily
- Spread through contact with aborted and live full term fetus, placenta, vaginal discharge, bodily fluids (blood, semen, urine), and in milk.
- Zoonotic
- Testing recommended if drinking milk raw.
Q Fever
- Caused by Coxiella burnetti bacteria
- Causes abortions, infertility, small or weak offspring
- Spread through dried aerosols (dust), contact with aborted and live full term fetus, placenta, vaginal discharge, bodily fluids (blood, feces, urine), and in milk.
- Zoonotic
- Testing recommended if drinking milk raw.
How to get your goats tested
Testing requires getting blood samples from your goats and submitting those samples to a lab. It's best to work with your veterinarian when possible.